If your mix sounds muddy, it’s likely due to frequency overlap, where multiple instruments compete in the same spectral space. This clash causes masking, making individual sounds hard to distinguish and creating a cluttered, unclear mix. To fix this, you can use EQ to carve out space for each element and panning to spread sounds across the stereo field. Keep learning the techniques below to achieve a clearer, more balanced mix.
Key Takeaways
- Overlapping frequencies among instruments cause masking, making individual sounds less distinguishable and creating a muddy mix.
- Excessive or poorly managed EQ boosts can increase frequency clutter, worsening muddiness.
- Lack of proper panning leads to crowded sonic space, intensifying frequency overlap and reducing clarity.
- Instruments competing for the same sonic range cause harmonic interference, resulting in a cluttered, unclear sound.
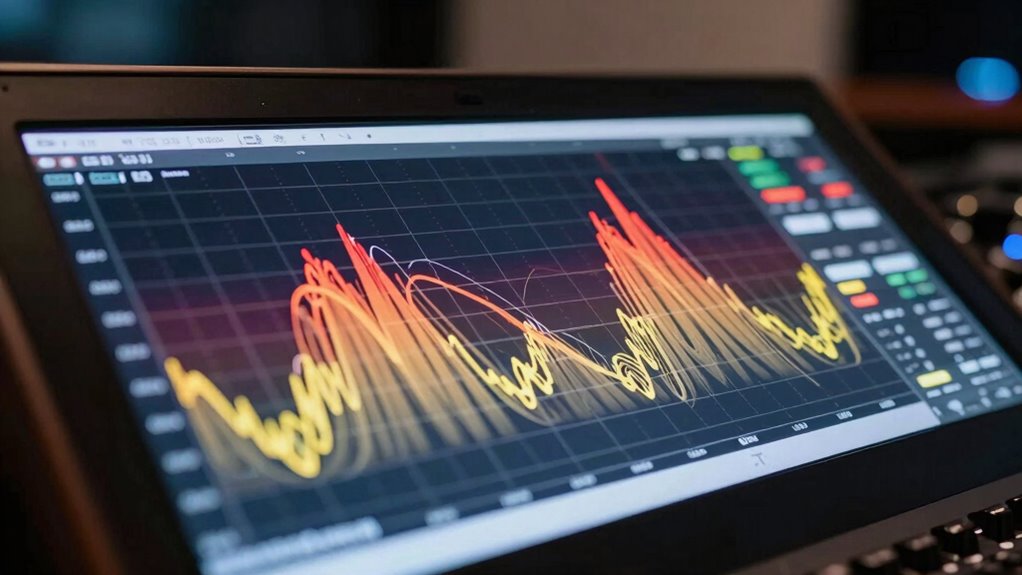
- Visual tools like spectrum analyzers help identify overlaps, enabling targeted adjustments to improve separation and clarity.
What Is the Frequency Overlap Problem in Mixing?

The frequency overlap problem occurs when two or more sounds in a mix share similar frequency ranges, causing them to compete for space and become indistinct. This is known as frequency masking, where one sound drowns out or dulls the clarity of another. As a result, your mix can sound muddy or cluttered because multiple elements clash within the same sonic space. The issue arises from sonic competition—when different instruments or vocals occupy overlapping frequencies, they fight for attention, making it difficult for each element to stand out. To avoid this, you need to identify and manage these overlaps, ensuring each sound has its own space in the frequency spectrum. Proper frequency management helps create a clearer, more balanced mix where every element is distinguishable.
How Do Multiple Instruments Clash in the Same Frequency Ranges?

When multiple instruments share the same frequency ranges, they can compete for space, causing sound masking. This overlap often leads to muddiness, making individual parts harder to hear clearly. Understanding how these clashes occur helps you make better mixing decisions to keep each instrument distinct. Incorporating proper equalization techniques can further reduce overlap and improve clarity in your mix.
Instrument Frequency Overlap
Multiple instruments often compete for the same frequency ranges, leading to clashes that can muddle sound clarity. When two or more instruments occupy similar frequencies, harmonic interference occurs, causing their sounds to blend or distort. This overlap results in tonal masking, where one instrument’s tone hides or diminishes another’s presence. For example, a guitar and a keyboard playing in the same midrange can obscure each other’s details, making the mix sound cluttered. To avoid this, you need to carefully carve out space for each instrument, reducing unnecessary overlap. Recognizing where frequency overlaps happen allows you to make precise EQ adjustments, ensuring each instrument retains its clarity without interfering with others. Sometimes, understanding the role of sound frequency in mixing can help you better allocate sonic space. This targeted approach keeps your mix clean and well-defined.
Masking and Clashing Sounds
In a mix, instruments often clash when their sounds occupy the same frequency ranges, causing masking that muddles clarity. This masking happens when multiple sounds compete within the same dynamic range, making it hard to distinguish individual parts. Clashing sounds can also affect stereo imaging, collapsing the perceived space and leaving your mix flat. For example, a snare and a vocal both occupying mid frequencies might mask each other, reducing clarity. To avoid this, you can use EQ to carve out space or adjust panning for better separation. Additionally, understanding frequency overlap can help you identify and minimize conflicts between instruments, ensuring a clearer mix. Here’s a quick overview:
| Instrument | Frequency Range | Clashing Effect |
|---|---|---|
| Electric Guitar | 1kHz – 3kHz | Masks vocals, reduces clarity |
| Bass Guitar | 60Hz – 250Hz | Overlaps kick drum |
| Lead Vocal | 1kHz – 4kHz | Clashes with guitars |
| Cymbals | 5kHz – 10kHz | Masking high-frequency instruments |
Why Does Frequency Overlap Make Your Mix Sound Muddy?

Frequency overlap causes your mix to sound muddy because multiple instruments or vocals compete for the same sonic space, making it difficult for each element to stand out clearly. When sounds share the same frequency range, they blend into a cluttered sonic mess. This is often caused by excessive instrument resonance or harmonic distortion, which can amplify certain frequencies and intensify overlaps. To prevent muddiness, focus on:
Frequency overlap muddies your mix by causing sonic clutter and reducing clarity.
- Identifying overlapping frequency ranges
- Reducing instrument resonance that clashes
- Controlling harmonic distortion to keep sounds clean
- Using EQ to carve out space for each element
- Incorporating vintage audio techniques to achieve a warmer, clearer sound.
How Can You Detect Frequency Overlap Using EQ and Analysis Tools?

To detect frequency overlap, you can use a spectrum analyzer to identify where multiple sounds occupy the same range. Recognizing clashing frequencies becomes easier once you learn to spot overlapping peaks and muddled areas. With effective EQ spotting techniques, you can isolate and reduce overlapping frequencies to clean up your mix. Understanding fandom’s past, present, and future can also help you anticipate how different elements might clash in your sound environment.
Spectrum Analyzer Application
Using a spectrum analyzer is one of the most effective ways to identify frequency overlap in your audio mix. It visualizes the spectral content, making it easier to spot areas of frequency masking and spectral clash. With this tool, you can see which frequencies are competing and causing muddiness. Look for overlapping peaks that indicate potential issues. To make the most of it, focus on:
- Identifying broad, congested frequency bands
- Spotting peaks that dominate or mask others
- Comparing tracks side-by-side for conflicts
- Monitoring how EQ adjustments affect frequency distribution
- Recognizing the importance of spectral resolution in accurately detecting overlaps
This real-time visualization helps you target problem areas precisely, ensuring you can clean up muddy mixes by reducing spectral clash and improving clarity. Using a spectrum analyzer streamlines the detection process, allowing you to make informed EQ decisions.
Recognizing Clashing Frequencies
When trying to detect overlapping frequencies, your goal is to identify areas where multiple sounds compete for the same spectral space. This is where frequency masking occurs, causing sonic collision that muddies your mix. Use a spectrum analyzer to visualize the frequency spectrum and spot regions with dense activity. Listen carefully for sounds that seem to hide or distort each other, indicating potential masking. EQ can reveal clashing frequencies by highlighting where sounds overlap, especially in the midrange and high-end. Sharp peaks or overlapping bands suggest sonic collision. By paying attention to these visual cues and sonic clues, you can pinpoint problematic areas, gaining insight into where your mix needs separation or adjustment to reduce masking and improve clarity. Additionally, understanding how SSD organization tips can streamline your workflow allows for more efficient use of analysis tools, making it easier to identify and address frequency overlaps quickly.
EQ Spotting Techniques
EQ spotting techniques allow you to identify frequency overlaps more effectively by analyzing your mix with precision. Using EQ and analysis tools helps reveal instances of frequency masking and harmonic conflicts that cause muddiness. By soloing individual tracks and gradually boosting or cutting specific frequency ranges, you can pinpoint where overlaps occur. Visual analyzers like spectrum analyzers or parametric EQ displays make it easier to spot problematic overlaps. Look for areas where multiple tracks display peaks at the same frequency, indicating potential masking. Additionally, listen carefully for clashing harmonics that muddy the sound. Here are effective techniques:
- Solo tracks to isolate overlaps
- Use spectrum analyzers for visual cues
- Boost and cut frequencies to test masking
- Identify harmonic conflicts through listening and analysis
Simple Techniques to Clear Up Frequency Overlap in Your Mix

Frequency overlap can muddy your mix and make individual elements less distinct, but thankfully, there are straightforward techniques to address this issue. One effective approach is to manage frequency masking by adjusting levels and EQ to reduce overlaps. Focus on giving each instrument its own space in the frequency spectrum, which helps prevent sounds from competing. Additionally, controlling the dynamic range allows you to emphasize important elements and prevent them from being buried under others. Using compression wisely can tame peaks and balance levels, ensuring clarity. Subtle EQ cuts in overlapping frequency areas help carve out space for each instrument. To further enhance separation, employing spectral analysis tools can help identify overlaps and guide precise adjustments. These simple techniques can profoundly improve separation, making your mix cleaner and more professional without overcomplicating the process.
How to Use EQ and Panning to Separate Instruments and Reduce Clutter

Using EQ and panning together is a powerful way to carve out space for each instrument in your mix. Proper instrument placement and panning techniques help prevent frequency overlap and clutter. Panning allows you to position instruments across the stereo field, giving each its own space. EQ sharpens this effect by reducing overlapping frequencies, making each element clearer. To maximize this approach:
- Use panning to spread instruments across the stereo spectrum
- Apply EQ to cut overlapping frequencies in busy instruments
- Place vocals and lead instruments centrally for focus
- Pan supporting instruments to complement the main elements
- Remember that free floating techniques can help in achieving a natural, spacious sound in your mix
Combining these techniques ensures your mix feels open and balanced, making each instrument stand out without fighting for space. This strategic use of panning and EQ creates clarity and reduces muddiness effectively.
Common Mixing Mistakes That Worsen Frequency Overlap

One common mistake that worsens frequency overlap is overusing EQ boosts, which can make the mix sound cluttered and harsh. This increases frequency masking, where multiple instruments compete in the same range, reducing instrument separation and clarity. Instead of boosting, try cutting problematic frequencies to carve out space. Be cautious with stereo panning; improper placement can compound overlap issues. Using narrow Q settings can help target specific problem areas without affecting the entire mix.
| Mistake | Effect | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Excessive EQ boosts | Cluttered sound, harshness | Use cuts and gentle boosts |
| Poor instrument panning | Reduced instrument separation | Pan instruments to create space |
| Wide Q settings | Unintended frequency overlap | Narrow Q for precise cuts |
Tips for Maintaining Clarity and Balance in Your Mix

Maintaining clarity and balance in your mix requires careful attention to how each element interacts within the overall soundscape. To reduce frequency masking and improve instrument separation, focus on strategic EQ adjustments. Use high-pass filters on non-bass elements to prevent unnecessary overlap. Create space by panning instruments apart, giving each its own sonic territory. Regularly solo tracks to evaluate how they sit together and identify overlapping frequencies. Ultimately, consider using dynamic processing to control harsh or muddy sounds. These steps help preserve clarity by minimizing frequency overlap and ensuring each instrument has room to breathe. With deliberate panning, EQ, and dynamic control, you can achieve a well-balanced mix where every element stands out clearly.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can Frequency Overlap Be Intentional in Certain Musical Styles?
Yes, frequency overlap can be intentional in certain musical styles. You actively use harmonic blending and stylistic overlap to create rich, layered sounds that define genres like jazz, reggae, or experimental music. By intentionally overlapping frequencies, you achieve a cohesive and immersive listening experience. Just be mindful of balancing these overlaps to avoid muddiness, ensuring each element still retains its distinct presence within the mix.
How Does Room Acoustics Influence Perceived Frequency Overlap?
Room acoustics dramatically influence perceived frequency overlap, making it seem more pronounced or less clear. You might think your mix sounds fine, but room resonance and speaker placement can cause certain frequencies to overlap or boost unexpectedly. By adjusting speaker placement and managing room resonance, you reduce unwanted overlaps, creating a clearer, more defined sound. Your mix will translate better across different environments, avoiding muddiness caused by acoustic interference.
Are There Specific Genres More Prone to Muddy Mixes Due to Frequency Issues?
Certain genres, like metal, EDM, and pop, are more prone to muddy mixes because of their dense arrangements and overlapping frequencies. You’ll notice that their genre characteristics often involve layered sounds and bass-heavy elements, which can cause frequency overlap issues. To avoid this, use specific mixing techniques such as EQ carving and careful panning, ensuring each element has its space and clarity in the mix.
What Are the Best Plugins for Detecting Frequency Overlap in Mixing?
You should use plugins like iZotope Ozone’s Spectral Analysis or FabFilter Pro-Q 3 for detecting frequency overlap. These tools provide spectral analysis and overlap visualization, making it easy to see where frequencies clash. By pinpointing problematic areas, you can adjust EQ and reduce mud. Active monitoring with these plugins helps you make precise cuts, resulting in a clearer, more balanced mix.
How Does Vocal Placement Affect Frequency Overlap With Instruments?
Did you know that proper vocal placement can improve instrument separation by up to 50%? When you adjust vocal positioning, you reduce frequency overlap with instruments, preventing clashes and muddy sounds. By placing vocals strategically in the stereo field and frequency spectrum, you help each element stand out clearly. This technique guarantees your mix sounds cleaner and more balanced, making every instrument and vocal line distinct and impactful.
Conclusion
To avoid muddy mixes, focus on managing frequency overlap carefully. Did you know that studies show about 60% of mixes suffer from clarity issues due to crowded frequency ranges? By using EQ, panning, and proper analysis tools, you can create space for each instrument, ensuring your mix stays clear and balanced. Remember, small adjustments make a big difference—so take your time and listen critically to achieve professional, polished results.